Wind Turbine
Wind turbines are an innovative way to capture the energy of the wind and turn it into clean electricity. Found in large wind farms around the world, these turbines are quickly growing in number, providing significant power for homes, businesses, and industries.
Why are wind turbines so important? They provide a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for generating energy. By using wind, we reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and help reduce pollution, which is crucial in the fight against climate change. Thanks to advances in technology, wind energy is becoming more affordable and accessible to countries everywhere.
In short, wind turbines represent a smart, renewable energy solution that not only powers our world but also protects the planet for future generations.

Benefits of Wind Power
- Clean, abundant, and inexhaustible fuel: Wind power produces no emissions and is not depleted over time.
- Local economic development: Wind plants can provide a steady flow of income to landowners who lease their land for wind development.
- Modular and scalable technology: utilities can use wind resources strategically to help reduce load forecasting risks.
- Wind energy is one of the cheapest of the renewable technologies while reducing reliance on imported fuels.
- Energy price stability: it reduces dependence on conventional fuels that are subject to price and supply volatility.
The disadvantage
While wind power offers numerous advantages, there are still challenges that need to be addressed for its broader adoption and integration. Issues such as intermittency, where wind speeds can fluctuate, and the need for efficient energy storage solutions, pose hurdles. Additionally, the impact of wind turbines on wildlife and local ecosystems, as well as the need for suitable land or offshore sites, must be carefully considered to ensure sustainable development.
Wind Turbines Come in
Two Configuration

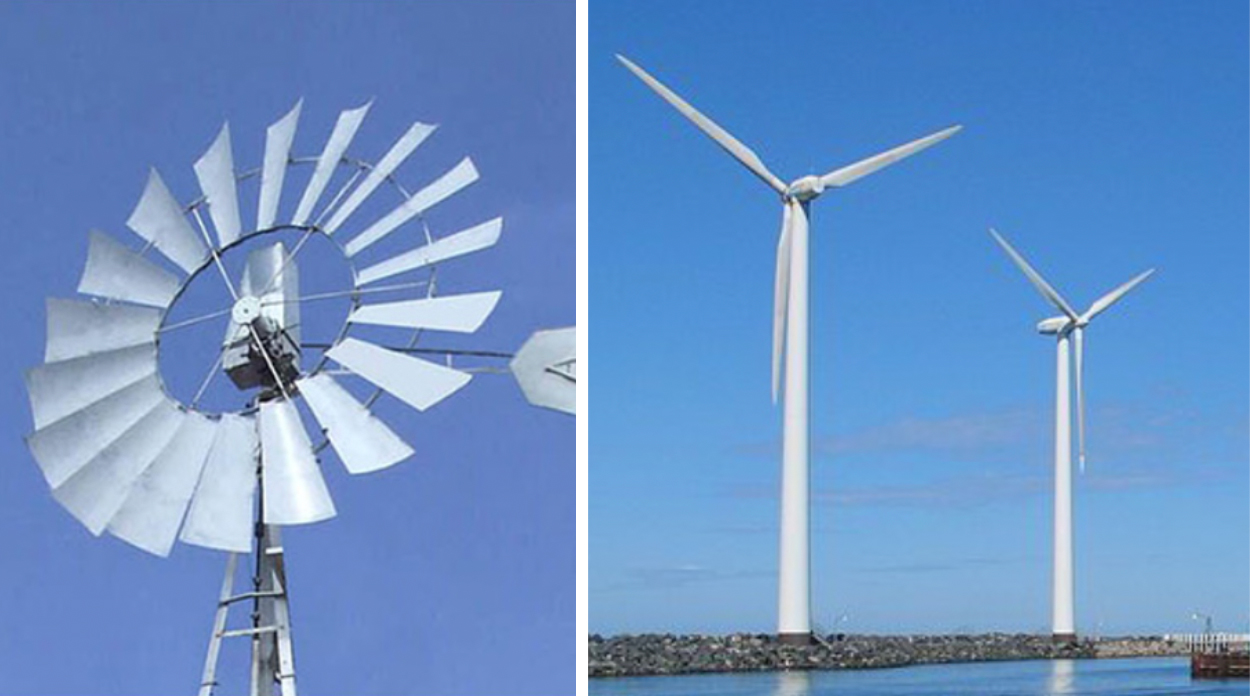
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine (HAWTs)
Most wind turbines used today are horizontal axis machines. To work effectively they must face the wind by using a tail that automatically orientates the turbines or by using motors to move the turbine

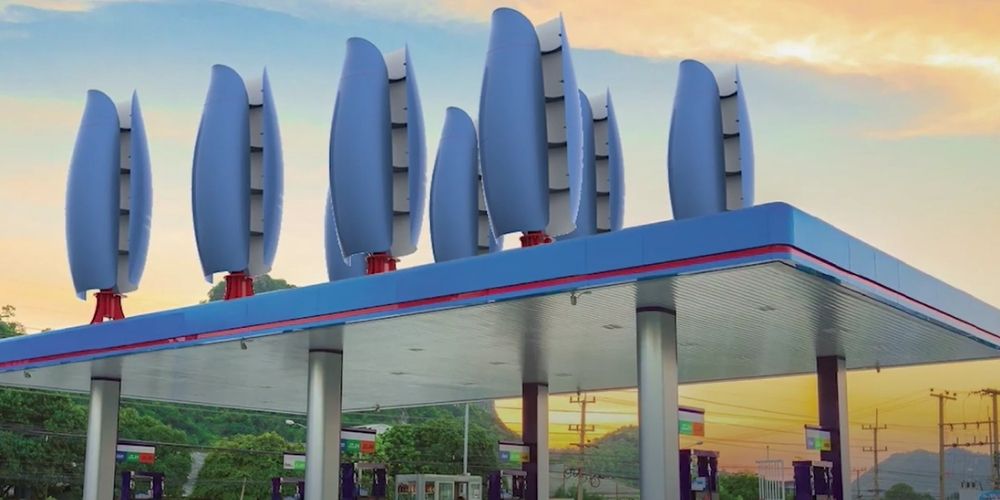
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)
Vertical axis turbines are cross-flow devices.
It will work with wind from any direction. They
are however less efficient at harnessing wind
energy.
Effect of Number of Blades
- Wind turbines with large numbers of blades have highly-solid swept areas and are referred to as high-solidity wind turbines.
- Wind turbines with small numbers of narrow blades are called low-solidity wind turbines.
- In theory, the more blades a wind turbine rotor has, the more efficient it is. However large numbers of blades can interfere with each other. High-solidity wind turbines tend to be less efficient overall than low-solidity turbines.
- Three-bladed rotors tend to be the most energy-efficient.
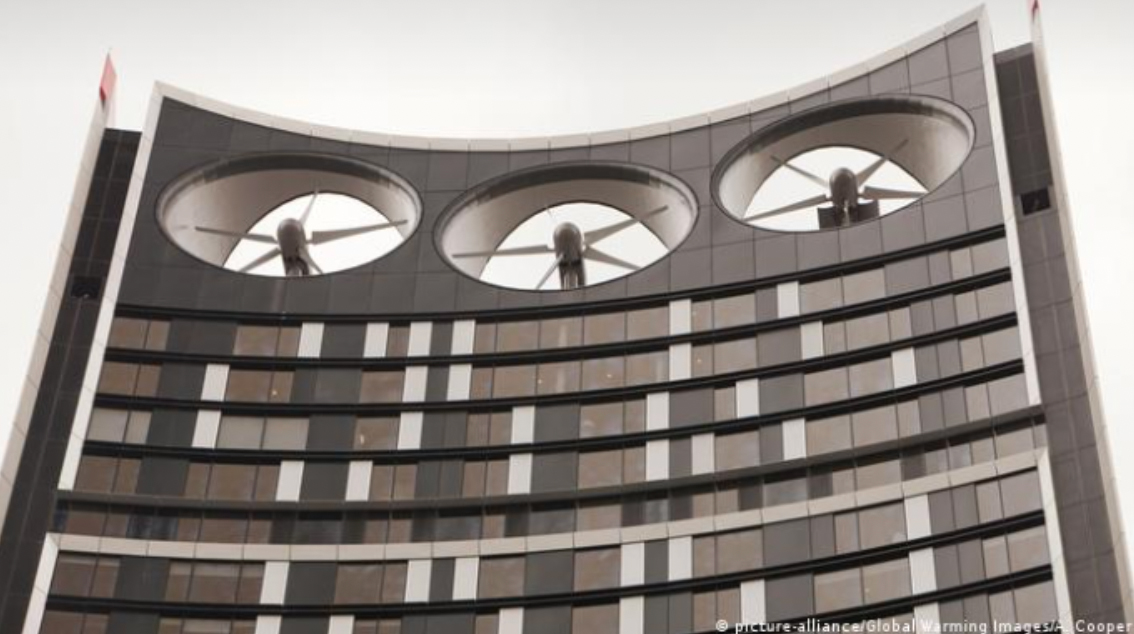
Building Mounted/Integrated Wind Turbines Advantages
- Height advantage without the need for large towers.
- Disturbed flows around buildings can locally increase wind speeds.
- Energy yields may therefore be increased relative to open sites.
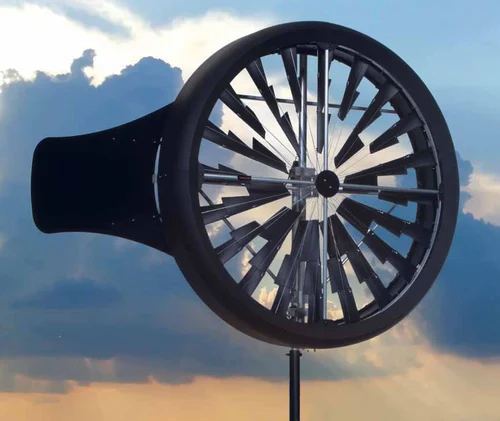
Ducted Wind Turbine
A ducted wind turbine is often installed on tall buildings to capture higher wind speeds. The turbine is housed in a funnel-shaped casing, which directs wind towards the blades, boosting efficiency. Positioned on rooftops, it avoids obstructions like other buildings, making it ideal for urban areas where wind speeds at ground level are lower.