Solar Thermal Collectors
Solar thermal collectors are essential components in renewable energy systems, designed to capture and utilize the sun’s abundant energy. Their main function is to absorb solar radiation, converting sunlight into heat or electricity, depending on the collector’s design and intended use.
These devices come in a variety of forms, each tailored to specific energy needs and utilizing different conversion methods. Their versatility allows them to adapt to diverse environments and energy requirements.
Solar collectors can be categorized into air-based and water-based systems. Air-based collectors, including both transpired and non-transpired types, use solar energy to heat air for space heating or industrial processes. Water-based collectors, like solar water heaters, absorb sunlight to heat water, serving domestic or industrial hot water needs.
Overall, solar collectors combine technological innovation with environmental consciousness. Their diverse forms and functions highlight their crucial role in transitioning to cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. With ongoing advancements in materials, design, and efficiency, solar collectors are shaping a greener, more energy-efficient future.

Solar Collector Types
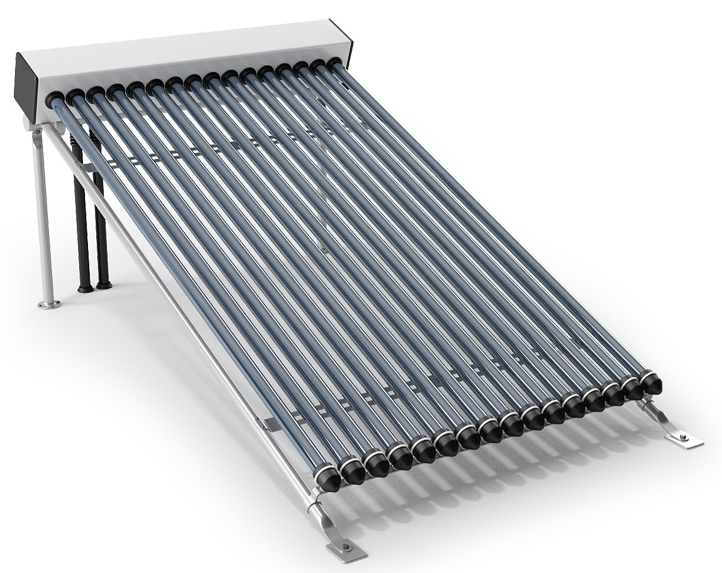

Air-Based (Transpired and Non-transpired Types)
A dark perforated absorber captures solar energy. The fan then draws in air through collectors of small holes and canopies. Later, the air is collected in a cavity between the solar collector and the building wall. The air is distributed through the building. The air has an improved quality at a low cost. The duct should be located near the south wall as part of the building envelope. Aluminum louvers (shading devices) are also used as solar thermal collectors.
Water Based (Non-concentrating and Concentrating)
These collectors absorb the sun’s radiation through a heat transfer liquid. The radiation is converted into useable heat energy by pumping the heat transfer liquid through a heat exchanger that transfers the energy to the water heater system.
- Non concentrating like solar ponds (solar radiation is absorbed and trapped on the bottom of the pond. temperature inversion due to density of salt water), flat plate and evacuated
- Concentrating like Trough, Dish and power tower
Domestic Types
Flat Plate Unglazed & Plastic Absorber Collectors
- Low cost
- Low temperature (0-10c rise)
- Rugged
- Lightweight
- Seasonal pool heating
- Poor performance in cold or windy weather
Flat Plate Glazed Collectors
- Simple construction
- Insulation and glazing prevent heat loss
- High-temperature operation (0-50c rise)
- Selective surface improves performance
- Moderate cost
- Heavy and bulky
- Easier to integrated
Evacuated Tube Collectors
- Very good at reaching high temperature (10-150c rise)
- No convection heat loss
- Difficult to integrate into roof
- Suitable for cold climates
- Fragile
- Cost more money than flat plate
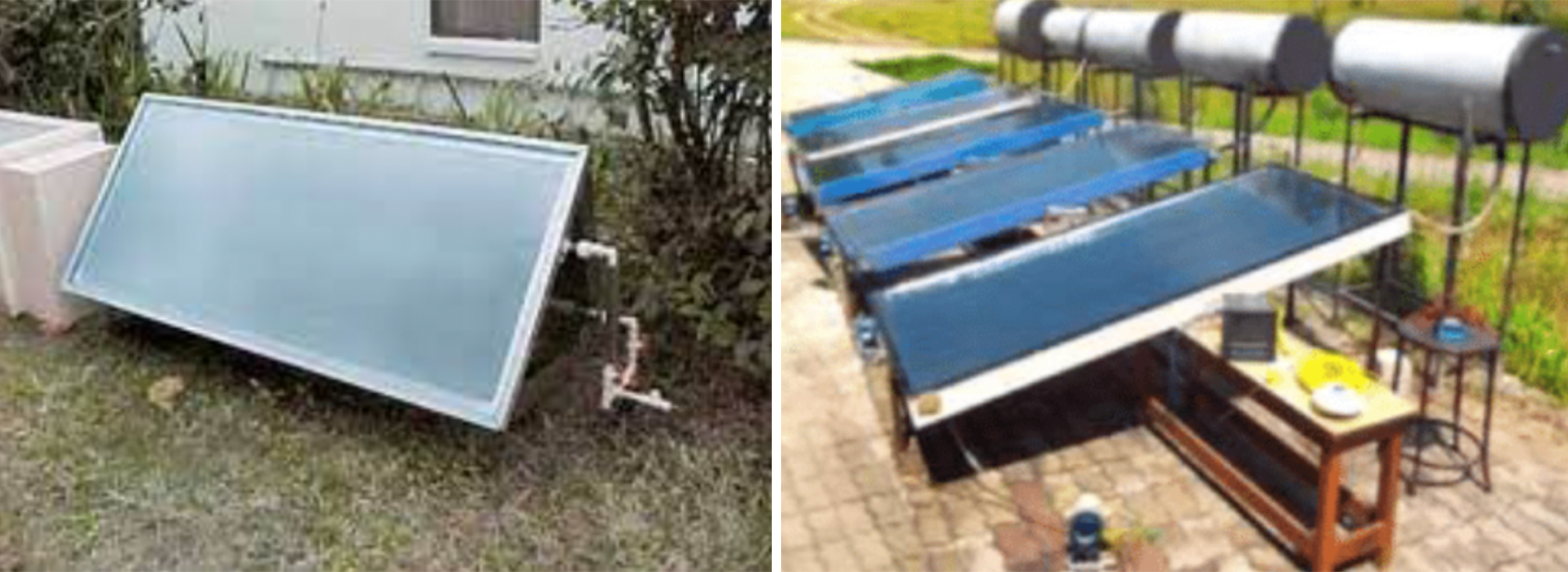

Passive: use gravity and tendency for water to naturally circulate as it is heated through the system without a pump. They are generally more reliable and easy to maintain.
- Batch Heater: these are the simplest solar hot water systems. Their simple design consists of a tank of water within a glass covered insulated enclosure carefully aimed at the sun.
- Thermosyphone Features: Natural circulation of water, Flat plate collector, Collector placed below the storage tank, Hot water is taken from the top of the tank
Active: active systems use electric pumps, valves, and controllers to circulate water or other heat transfer fluids through the collectors. Active types are two models.
- Direct Systems: Circulate water directly through solar collectors for heating.
- Indirect Systems: Use a heat transfer fluid that passes through a heat exchanger to warm the water.
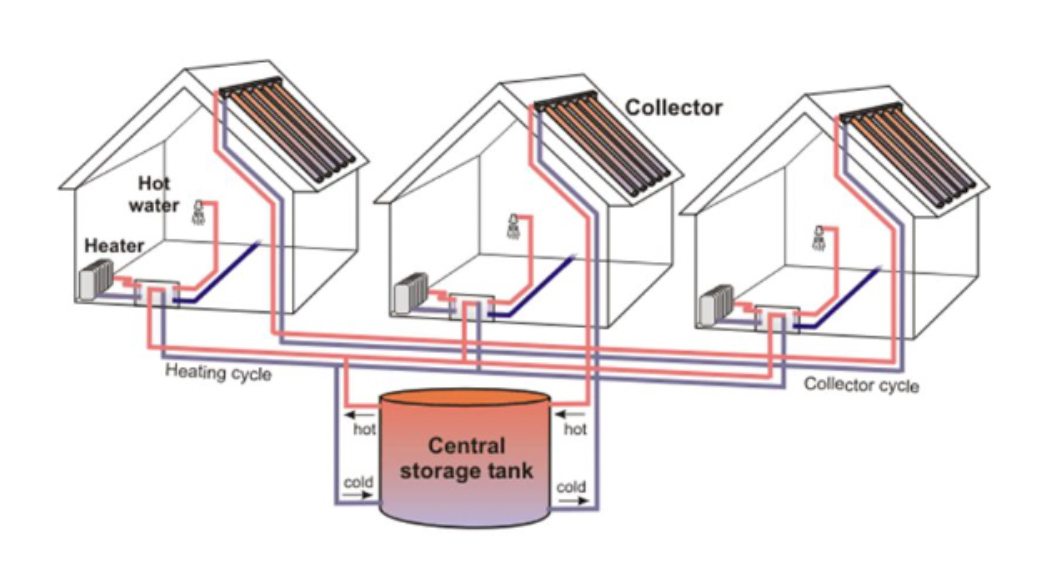
Solar District Heating Systems
The surface-to-volume ratio of a central storage tank is much better than that for distributed storage systems. So the storage losses are much lower and even permit seasonal heat storage. Solar district heating is also an option if room heating is to be covered by solar energy. Nevertheless, there are higher piping losses with a central tank.